Over the past few years, the
data storage market has changed radically. The traditional hierarchy of
directories, sub-directories, and files
referred to as file storage has
given way to object storage, individual storage
objects. While file storage was designed to help humans interact with data,
object storage is all about automated efficiency.
User expectation of data usage drives file storage repository
design. In this structured data model, all folders
and names are organized to support a pre-defined business process or model. The
file system also associates a limited
amount of metadata (i.e., file name, creation
date, creator, file type) with the saved file. Finding individual files is done
either manually or programmatically by working through the hierarchy. The file storage approach works well with data
collections but can become very cumbersome as data volume grows.
Object storage, on the other hand, is optimized for an unstructured data model. While this approach is not “human-friendly”
it also doesn’t require prior knowledge or expectations of data use. Files are
stored as objects in various locations with a unique identifier and a significant
amount of metadata. The size of the accompanying metadata can range from kilobytes
to gigabytes and often includes a content summary, keywords, key points, comments, locations of associated objects,
data protection policies, security, access, geographic locations and more. Enhanced
metadata enables a lower level of
granularity when protecting, manipulate, and managing stored objects.
Specific business,
technology, and economic drivers caused this significant market change. Business
drivers include:
- Rapid growth in amount and importance of unstructured data
- Need to implement faster data retrieval based on identifying details incorporated in metadata that the operating system reads.
- The requirement to apply organization to unstructured data resource through the use of text analytics, auto-categorization, and auto-tagging.
- Increased legal and regulatory requirements for scalable data archiving and e-discovery
- Enhanced business process and model flexibility enabled by the use of a flat storage structure.
From a technical point of view, object storage is far
superior to file systems. This advantage
is primarily due to its unlimited scalability and ability to be managed
programmatically. It also:
- Has fewer limitations when compared to the traditional file or block-based systems because of the flat data environment
- Ability to customize metadata through arbitrary use of any number of data attributes
- Global accessibility using HTTP(S) and REST APIs
From an economic point of view, object storage is also more cost-effective than file storage solutions,
especially when storing large amounts of data. Since object storage solutions efficiently leverage unlimited scalability,
organizations find that it is less costly
to store all of their data. This advantage also exists in private cloud implementations where costs
can be even lower than that provided by public cloud providers.
Object storage is also much more durable than file-based
alternatives.
The
marketplace offers plenty of alternatives
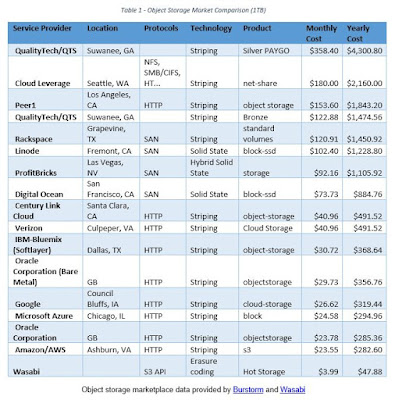
when object storage is the right answer. Access protocols, technology, and cost, however, varies widely. As shown in
Table 1, storage cost for 1 terabyte of data for one year ranges from a high of
$4,300.80 with data
striping from QualityTech/QTS to a low of $47.88
from Wasabi
that uses a more advanced erasure coding
approach. While location differences cause some
cost variation, most of the variation can be attributed to design
architecture and underlying storage technology.
Although this market survey is
not exhaustive by any means, it highlights the importance of being an
educated consumer when considering object storage solutions. Other solutions aspects worth investigating
include:
- Complexity and performance across provider storage service tiers
- Data immutability and durability
- Speed of internal consistency across multiple copies of your data
- Elapsed time to the delivery of the first byte of requested data
- Use of active integrity checking
By all objective accounts, object storage is the right
storage for large segments of an organization’s data holdings. This reality
should lead to more effective due
diligence and care when considering your enterprise’s next storage upgrade.
( This content is being syndicated through multiple channels. The opinions expressed are solely those of the author and do not represent the views of GovCloud Network, GovCloud Network Partners or any other corporation or organization.)
( Thank you. If you enjoyed this article, get free updates by email or RSS - © Copyright Kevin L. Jackson 2018)



1 comment:
Thank you so much for this nice information. Hope so many people will get aware of this and useful as well. And please keep update like this.
Text Analytics Software
Text Analytics with R
Post a Comment